Activist investing is a powerful driver of corporate transformation. The core objective of activist investors is to enhance a company's performance, thereby increasing its share price and generating returns on their investment. As activist investor Carl Icahn remarked, “You better get that price up, or someone else will do it for you” (Mark Maffett, 2022).
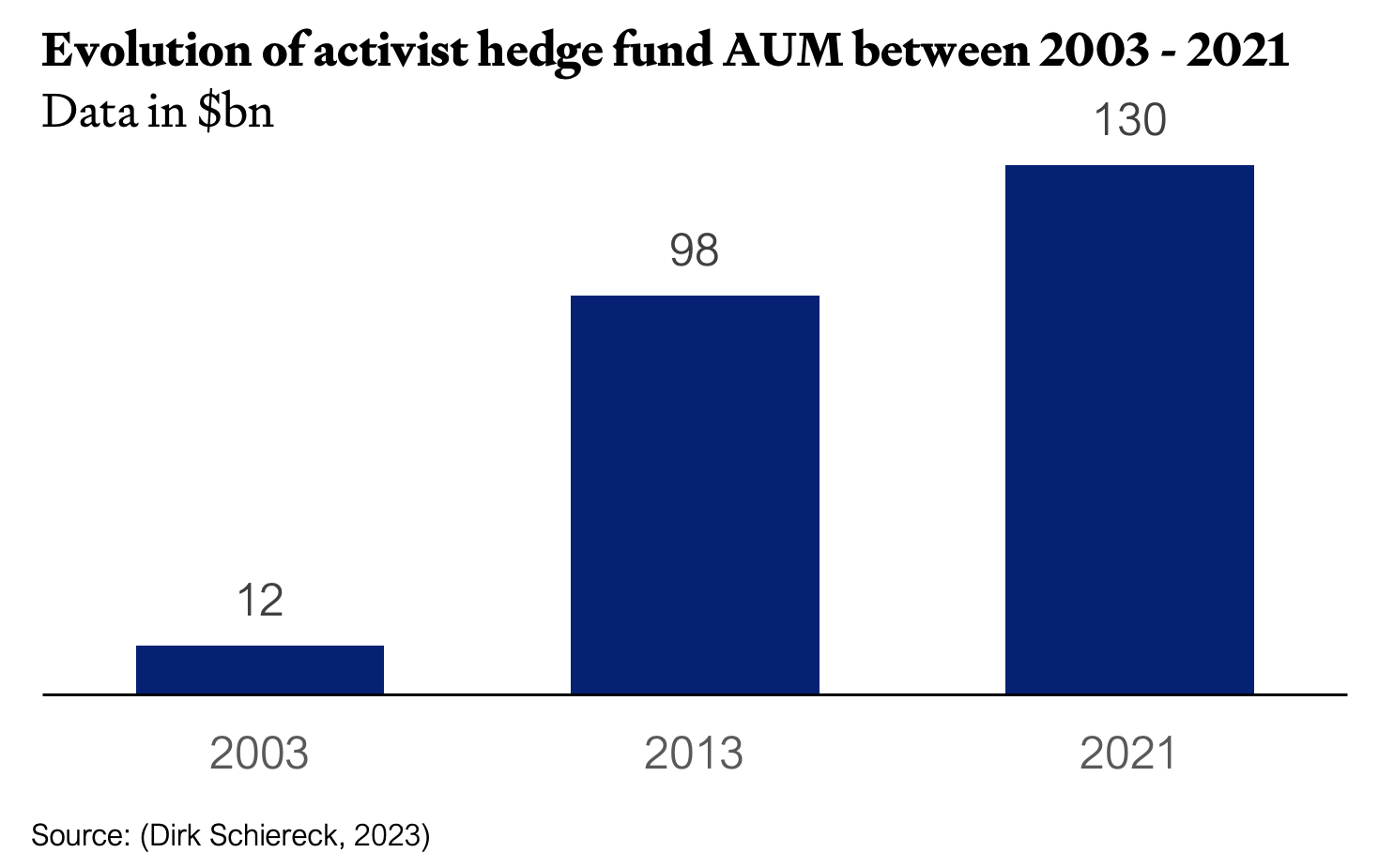
Activist investing has experienced significant growth over the years. Between 2000 and 2014, the number of activist investor campaigns increased by 34% annually. The assets under management (AUM) in activist hedge funds (AHFs) have also expanded considerably, rising from $12bn in 2003 to $93bn within a decade and reaching approximately $130bn by 2021 (Dirk Schiereck, 2023). Between 2011 and 2015, activists targeted nearly half of the companies listed in the S&P 500. In 2014 alone, they launched 344 campaigns against public companies, and overall, 26% of U.S. companies were targeted at least once by an activists. Notably, environmental activism has gained prominence, extending beyond U.S.-based firms and increasing its influence in other regions. The momentum of activist investing remains strong. In 2022–2023 alone, 1,139 activist campaigns were launched globally, underscoring the sustained impact and growing reach of activist investors.

One of the most notable cases involved Engine No. 1, an activist fund founded by Christopher James, in a high-profile proxy battle against ExxonMobil’s management. Despite holding just 0.02% of the company’s voting shares, Engine No. 1 successfully secured three seats on the board of directors. This strategic victory pressured ExxonMobil to shift its corporate focus toward renewable energy, increasing investments in wind and solar power. This case highlights a key tactic employed by activist investors: acquiring a minority—but strategically significant—stake to influence corporate governance and drive strategic changes. By targeting underperforming companies relative to their competitors, activist investors play a critical role in enhancing shareholder value and improving overall corporate performance (Schüler, 2016).
This development prompts several key questions: What critical factors influence their target selection process? How does their engagement affect the performance of target firms?
Activist investors typically target companies with low market capitalization, high institutional ownership, strong liquidity, and lower valuation multiples (Edward P. Swanson, 2022).
In recent years, particularly in the U.S., there has been a growing focus also on larger corporations, becoming the target of choice in ¼ of the cases. Activist hedge funds primarily seek undervalued companies, those whose market value significantly lags behind their potential value. This potential value is assessed by comparing similar companies of equivalent size operating in the same market. To unlock this hidden value, activists invest in these firms and push management to implement strategies that enhance shareholder returns
Several other factors influence the likelihood of a company being targeted by activists. Firms led by female CEOs are 52% more likely to be targeted compared to those led by male CEOs. Additionally, firms with higher-than-average CEO compensation relative to their peers face an increased probability of activist intervention (Dirk Schiereck, 2023). In Europe and specifically in Germany, activists tend to favour smaller firms with dispersed ownership, strong financial visibility, robust sales growth, high profitability, lower leverage, broad diversification, and substantial institutional ownership (Wolfgang Bessler, 2022). Poor corporate governance also makes companies more attractive targets.
Moreover, activists are more likely to engage with firms that have high analyst coverage, as this provides greater transparency and insight into future performance, making the company more appealing to investors. Stock liquidity is another crucial factor, firms with higher liquidity are more attractive because activists typically acquire large shareholdings in a short period. Low liquidity can make it difficult to secure a significant stake quickly – and exit the stake when the time comes.
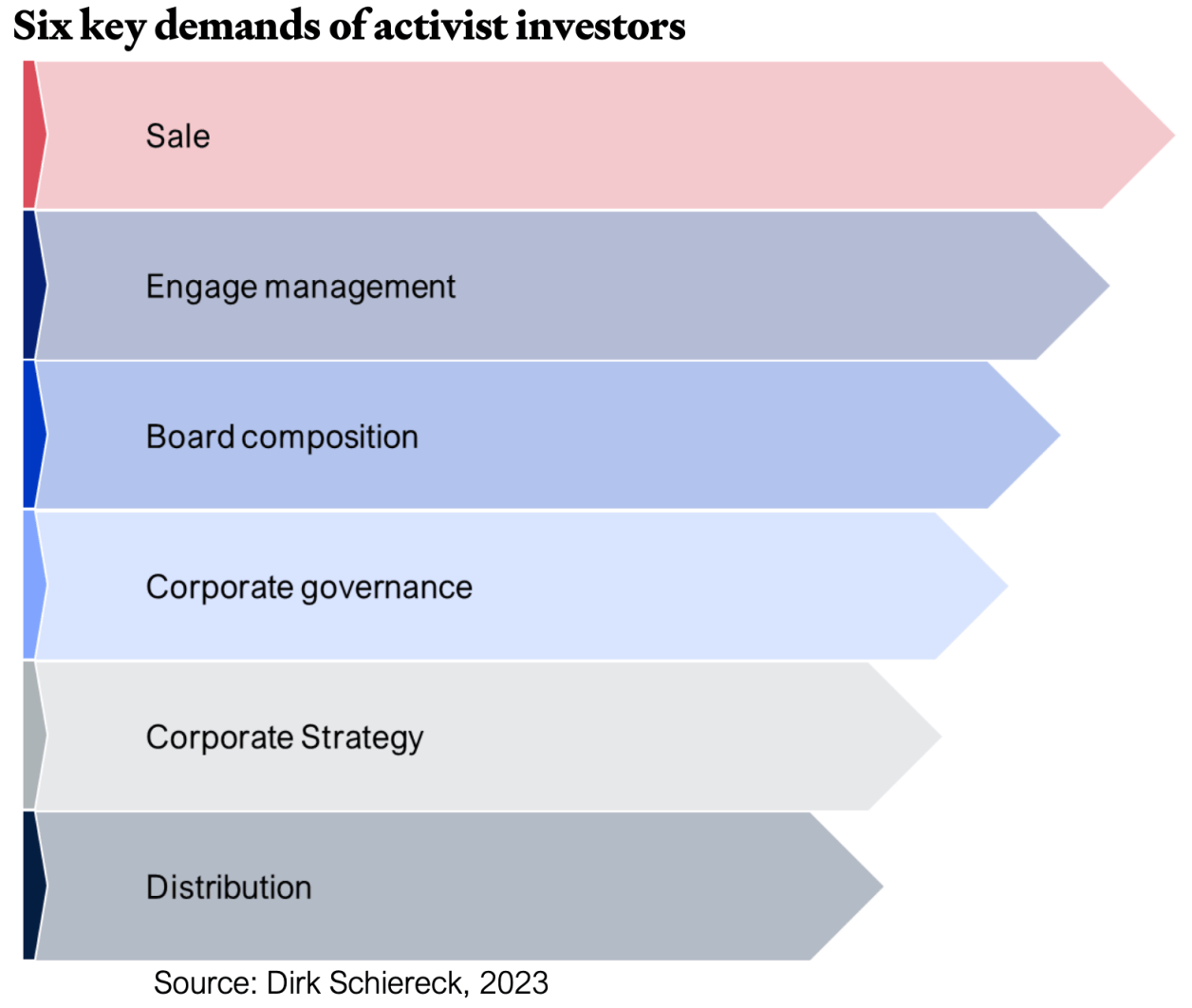
Activist investors pursue various demands to enhance shareholder value. These demands generally fall into six categories (Dirk Schiereck, 2023):
• Sale demand – This occurs when an activist investor pressures the company to sell itself or divest certain assets, either to the investor or a third party.
• Engage Management – Activist investors seek direct communication with management to discuss opportunities for improving shareholder value.
• Board composition changes – Investors may push for board representation by appointing new directors or demanding the resignation of existing members.
• Corporate governance reforms – Beyond board changes, activists may advocate for increased transparency, the removal of takeover defenses (e.g., poison pills), and other governance enhancements.
• Corporate strategy adjustments – Investors may push for modifications in corporate strategy, such as optimizing the company’s capital structure for tax efficiency or eliminating unprofitable product lines.
• Distribution – Returning excess cash to shareholder by either increasing dividends or starting a share repurchase programme.
Among these demands, sale demands generate the highest shareholder value (Edward P. Swanson, 2022). Notably, companies with higher passive ownership levels face a greater likelihood of being targeted for sale. Board composition demands are common in activist campaigns. Among activist campaigns against U.S. companies more than 1/3 result in at least one board seat or the ability to appoint a new director. Securing board representation is one of the most effective activist strategies for improving firm profitability. However, if activists gain full board control, the positive profitability effects diminish, potentially eroding earlier gains.
The CEO shuffle: Activist investors are driving executive exits
CEO turnover is another key outcome of activist investor interventions. When activists target U.S. firms, the likelihood of a CEO being replaced within two years of investment rises to 39%, compared to the general replacement rate of 28% (Wonik Choi, 2020). Overall, approximately 47% of CEOs at activist-targeted firms were replaced. Executive search firm Russell Reynolds Associates, which monitors CEO turnover across 13 global stock market indices, reported that 202 chief executives of major publicly listed companies stepped down last year, a 9% increase from 2023. Among these departures, 43 executives left within 36 months of assuming their roles, the highest figure since 2018. The report attributed this trend to diminishing patience among activist investors for underperformance. The technology sector experienced the highest CEO turnover rate of any industry in 2023, largely driven by the disruptive impact of artificial intelligence. 40 technology CEOs exited their positions, representing a 90% increase from the previous year. Notable departures included Pat Gelsinger, who resigned as Intel’s chief executive amid mounting investor pressure over his strategic vision for the company's turnaround.
The CEO role is becoming less attractive, the global pressure is intensifying, scrutiny is increasing, and as a result, we are seeing fewer serial CEOs. Most newly appointed chief executives in 2024 were “step-up” candidates, executives advancing from roles such as chief operating officer, assuming the top leadership position for the first time. Additionally, there has been a growing trend of finance leaders transitioning into CEO roles in recent years, as companies increasingly prioritize cost-cutting and operational efficiency (Raval, 2025).
Given the significant impact on CEOs and corporate strategies, do the initiatives advocated by activist investors effectively enhance shareholder value? The assessment of activist investors' performance remains inconclusive due to inconsistencies in existing research. While the majority of authors report a significant short-term increase in stock performance based on financial metrics such as stock price, returns, and abnormal returns, the long-term impact remains uncertain. As activist investors continuously adapt and refine their strategies to achieve superior abnormal returns, their performance dynamics are in constant flux.
Associate
Managing Partner
Dirk Schiereck, J. V. (2023). Activist investors: A literature review on recent evidence. Corporate Ownership & Control.
Edward P. Swanson, G. M. (2022). Are all activists created equal? The effect of interventions by hedge funds and other private activists on long-term shareholder value. Journal of Corporate Finance.
Mark Maffett, A. N. (2022). Importing activists: Determinants and consequences of increased cross-border shareholder activism. Journal of Accounting and Economics.
Raval, A. (2025, January 29). Record number of CEOs leave roles amid activist pressure, research shows. Financial Times.
Schüler, P. (2016). Shareholder Activism in Continental Europe. Technische Universität Darmstadt.
Wolfgang Bessler, M. V. (2022). Corporate control and shareholder activism in Germany: An empirical analysis of hedge fund strategies. International Review of Financial Analysis.
Wonik Choi, J. J. (2020). Hedge fund activism, CEO turnover and compensation. Journal of Accounting and Public Policy.
Free AI Website Maker