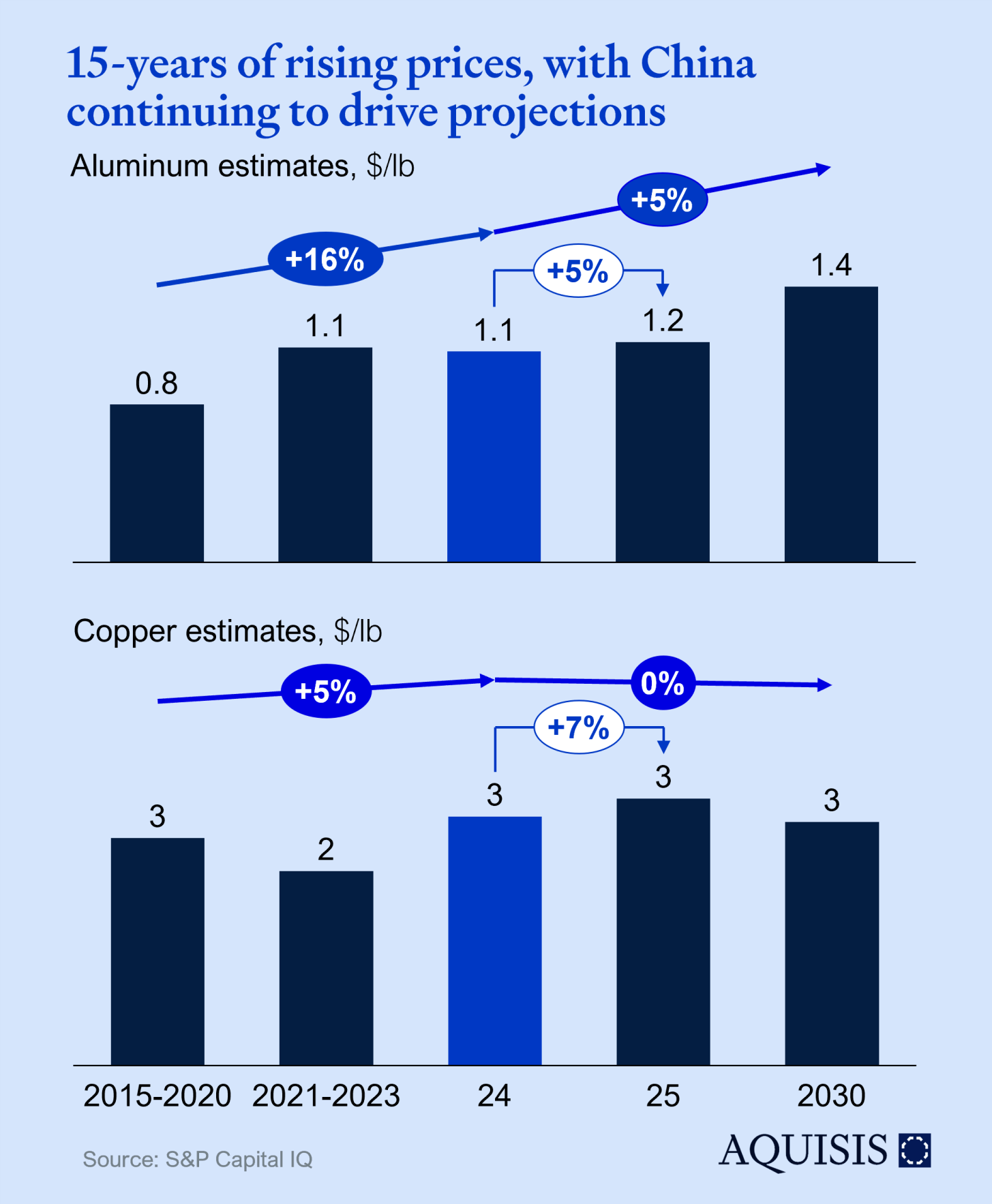
Aluminum is forecasted to rally until 2030, over concerns on inventory shortage. This anticipates a tightening market with demand outpacing supply, driven by the global transition to renewable energy and electric vehicles. Goldman highlighted that the impact of China's economic growth on metal prices is more pronounced than on oil and coal due to China's significant role in global metals demand.
Copper is projected in a flat to negative trendline from 2024 sparking a wave of pessimism about the medium-term outlook for a metal used in everything from renewables to power grids. Global inventories of copper have risen to their highest level in four years as weak demand has led to a glut of metal entering into warehouses all the while exploration budgets have been historically high.
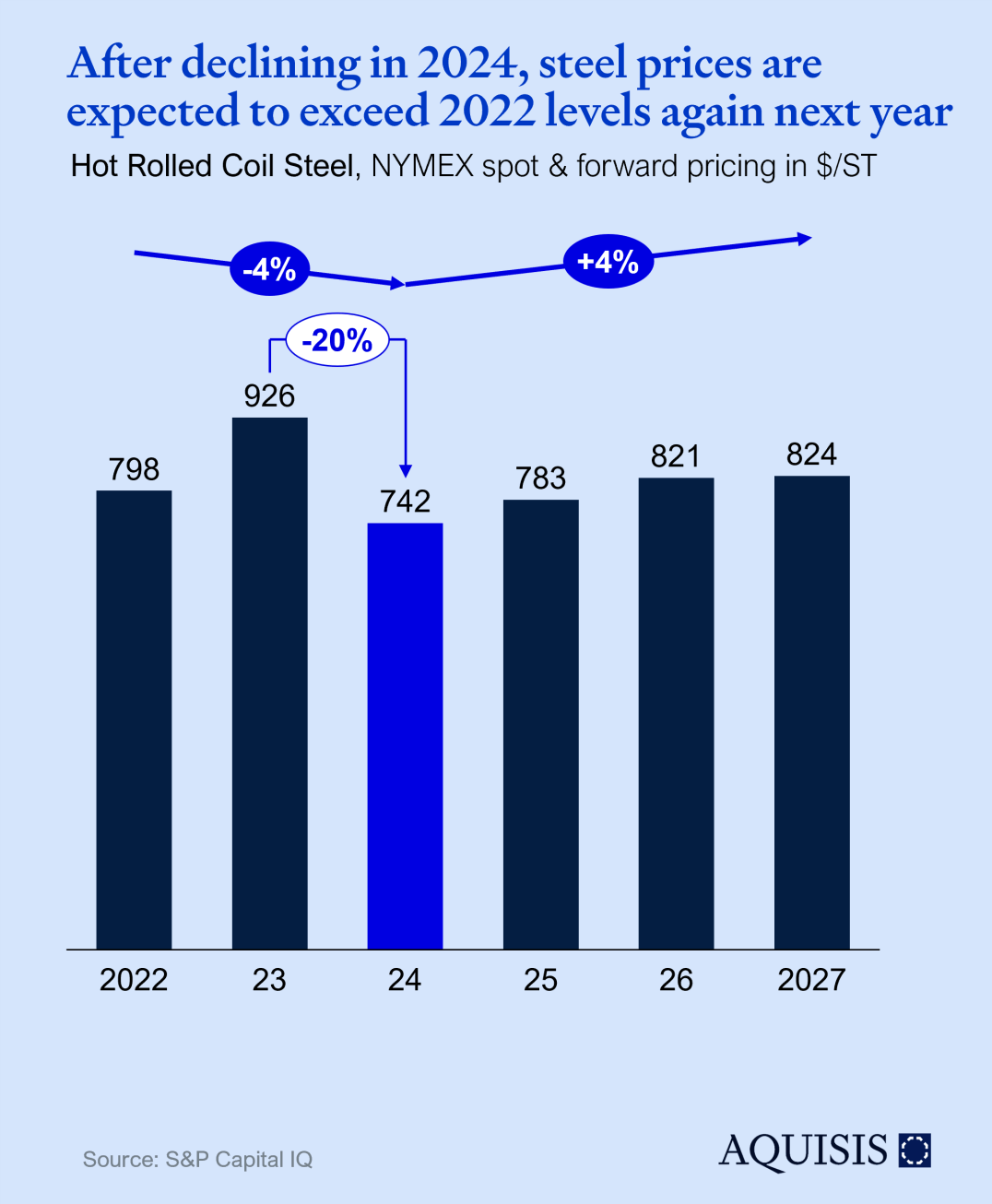
As of the time of writing, Hot Rolled Coil Steel (NYMEX) was trading at $679, while futures for December 2027 stood at $824, reflecting a projected 21% price increase over the next three years, with the majority of this growth anticipated to occur in 2025. This upward trend indicates a market poised for recovery after a period of subdued pricing driven by diminished demand in China and ongoing challenges within key steel-consuming sectors, particularly automotive manufacturing.
However, analysts expect these factors to gradually normalize as global economic conditions stabilize, with China's industrial recovery playing a pivotal role. Additionally, shifts in supply chains, including efforts to decarbonize steel production, could introduce further upward pressure.
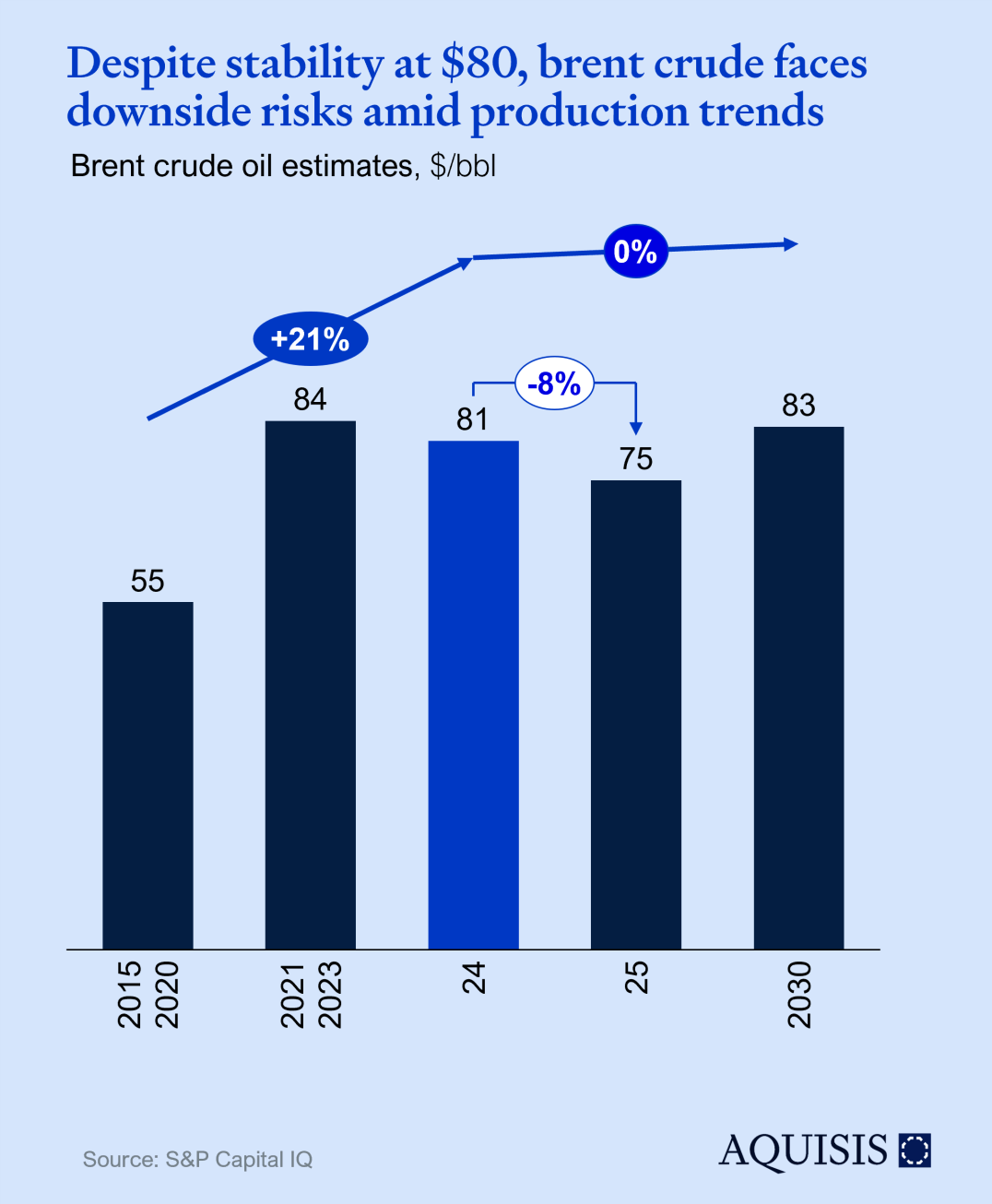
Following a significant surge since 2022, prices have stabilized at approximately $80 per barrel in 2024. However, this stability could shift if Iranian energy infrastructure were to sustain damage. Adding to the complexity, global oil inventories are significantly lower, currently at 4.4 billion barrels, the lowest level recorded since January 2017.
Looking ahead, Brent crude oil prices are more likely to decline than rise, as global oil production is expected to exceed forecasts rather than fall short. Forecasts expect $75/bbl while futures at the time of writing indicate $70/bbl at the end of 2025. That said, the potential for prices to exceed current projections hinges largely on unplanned production disruptions, a risk underscored by escalating tensions in the Red Sea.
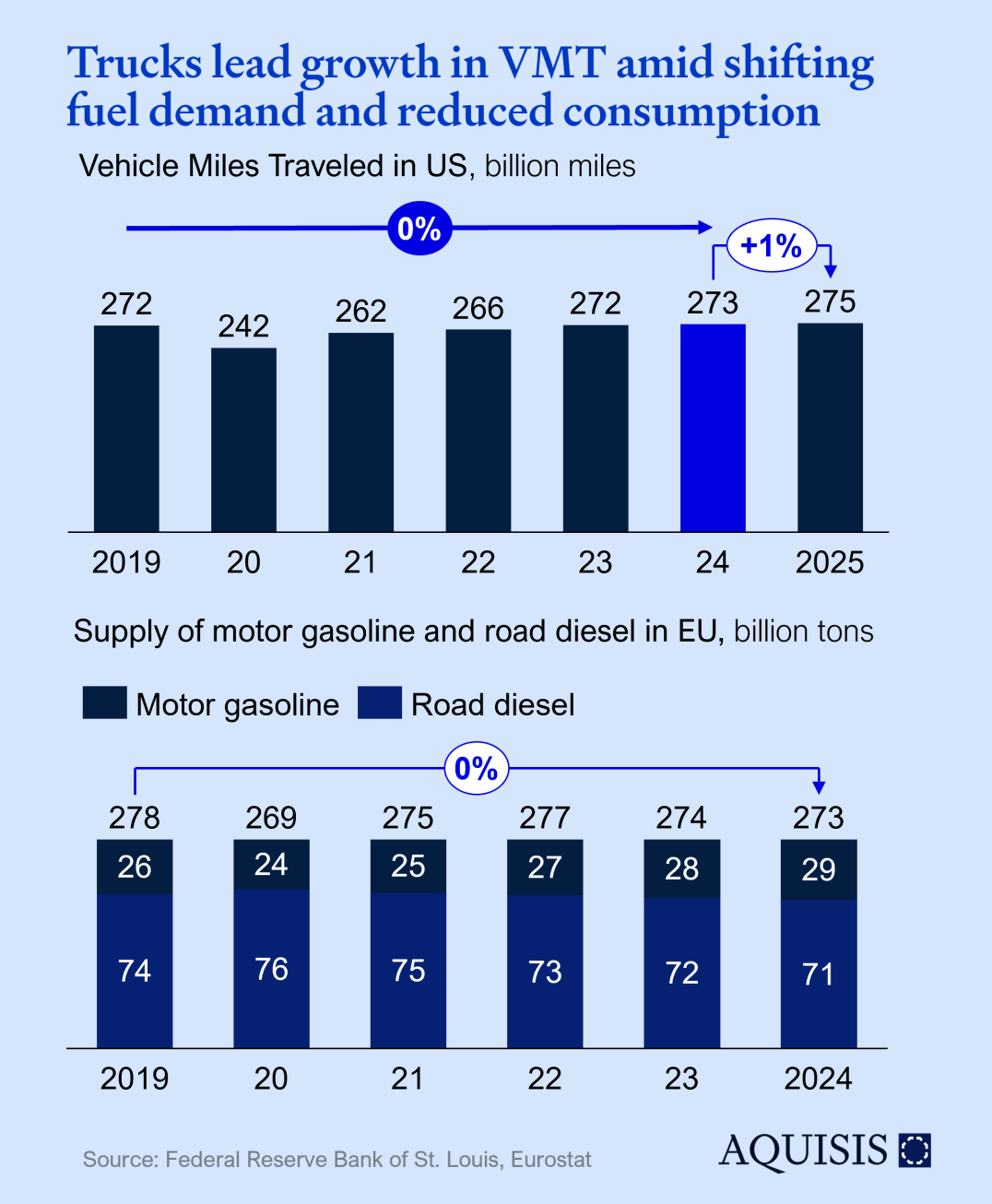
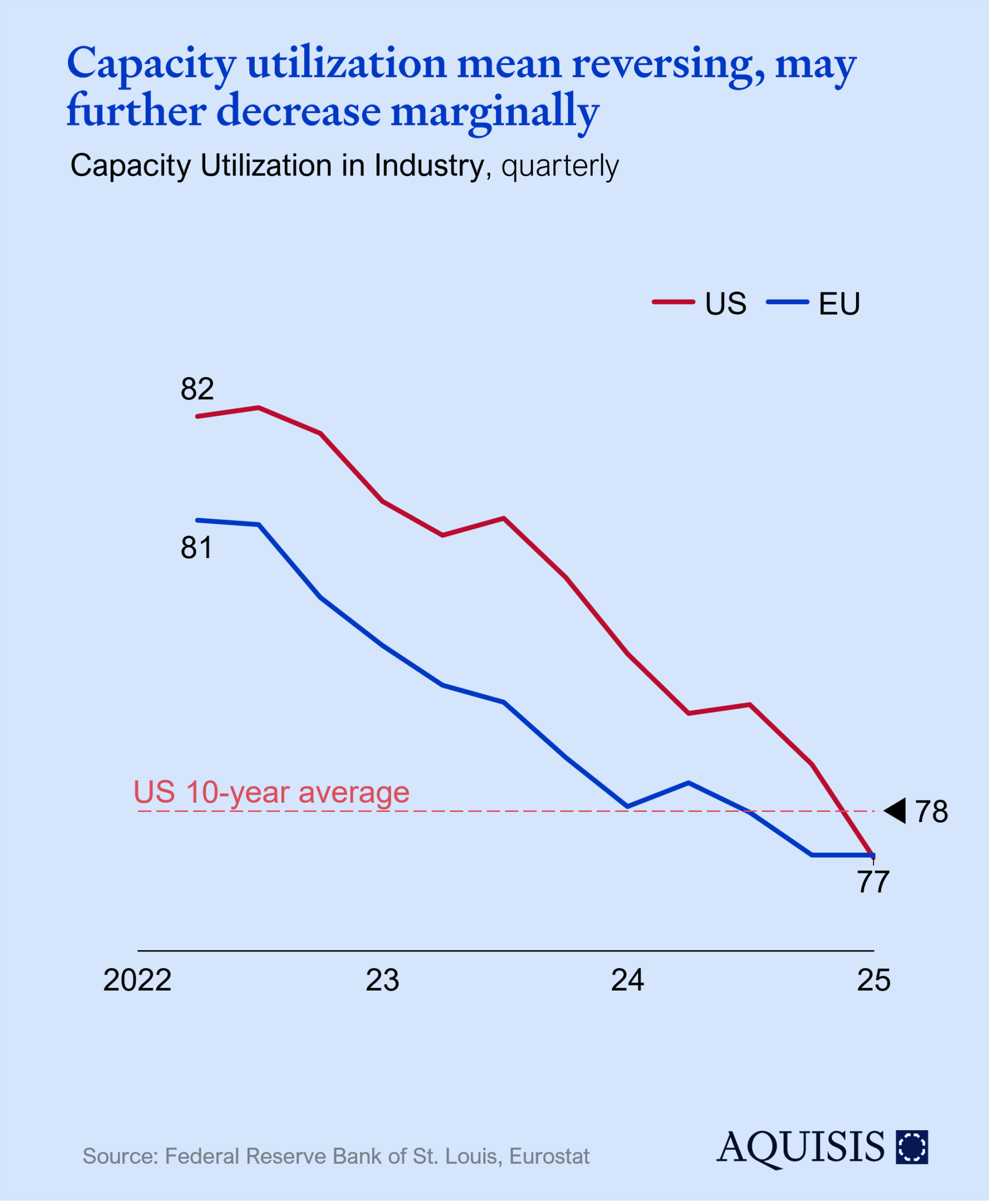
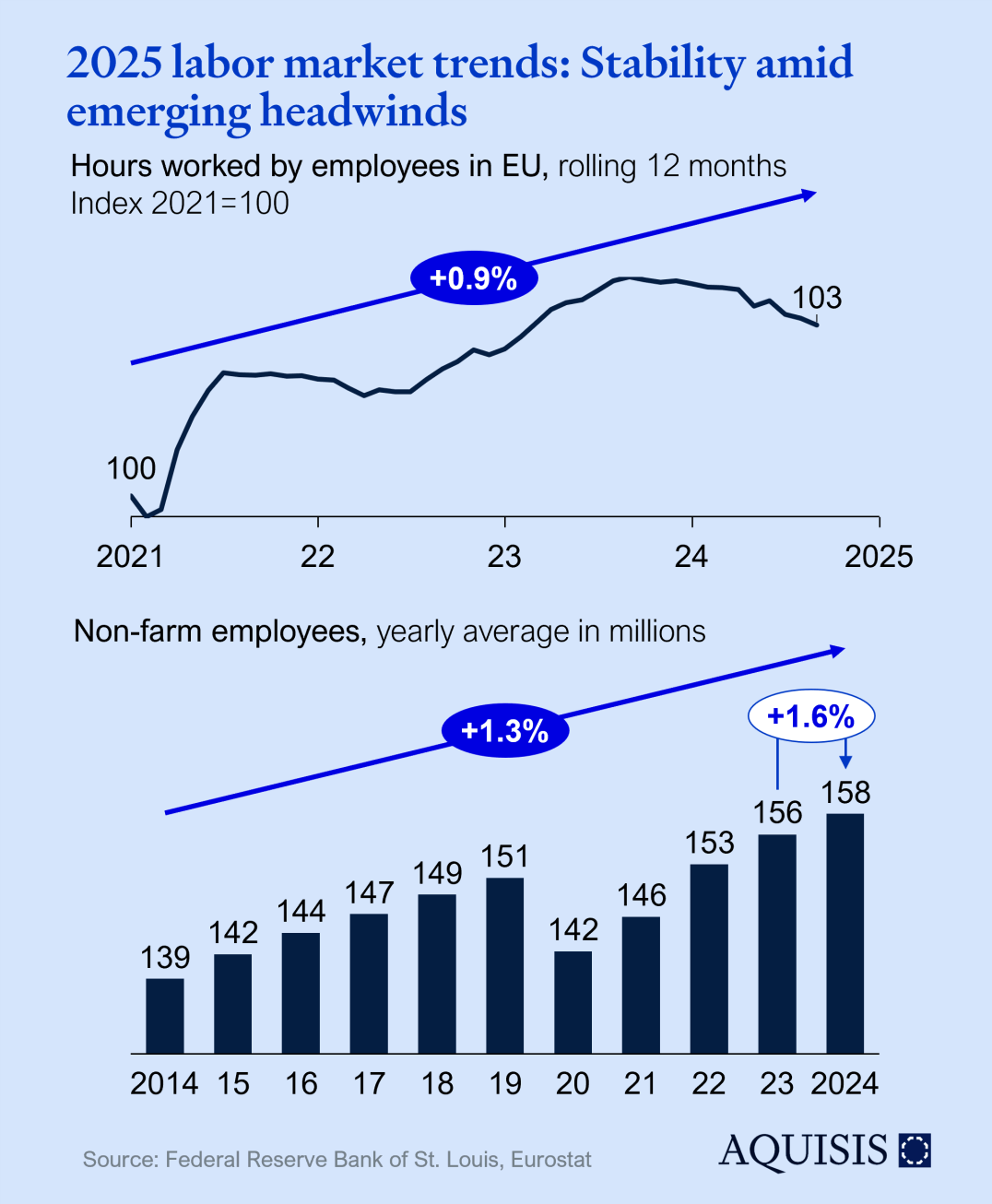
Capacity utilization is one of the most watched leading indicators. European utilization has more or less stabilized at 77-78% since Q4-2023 with the US only reaching that level in Q4-2024. While certainly not a positive signal, the current level is close to the 10-year average of the US; a positive take would therefore be one of normalizing after Covid, Ukraine, and the supply chain crisis. We do not believe a linear extension of the past 3 years is in store for 2025, although a slight softening towards 76% can’t be excluded.
Longer term structural effects like the West’s deindustrialization or the European automotive value chain’s malaise may exert downward pressure but tend to show up as reduction in capacity rather than short-term utilization effects.
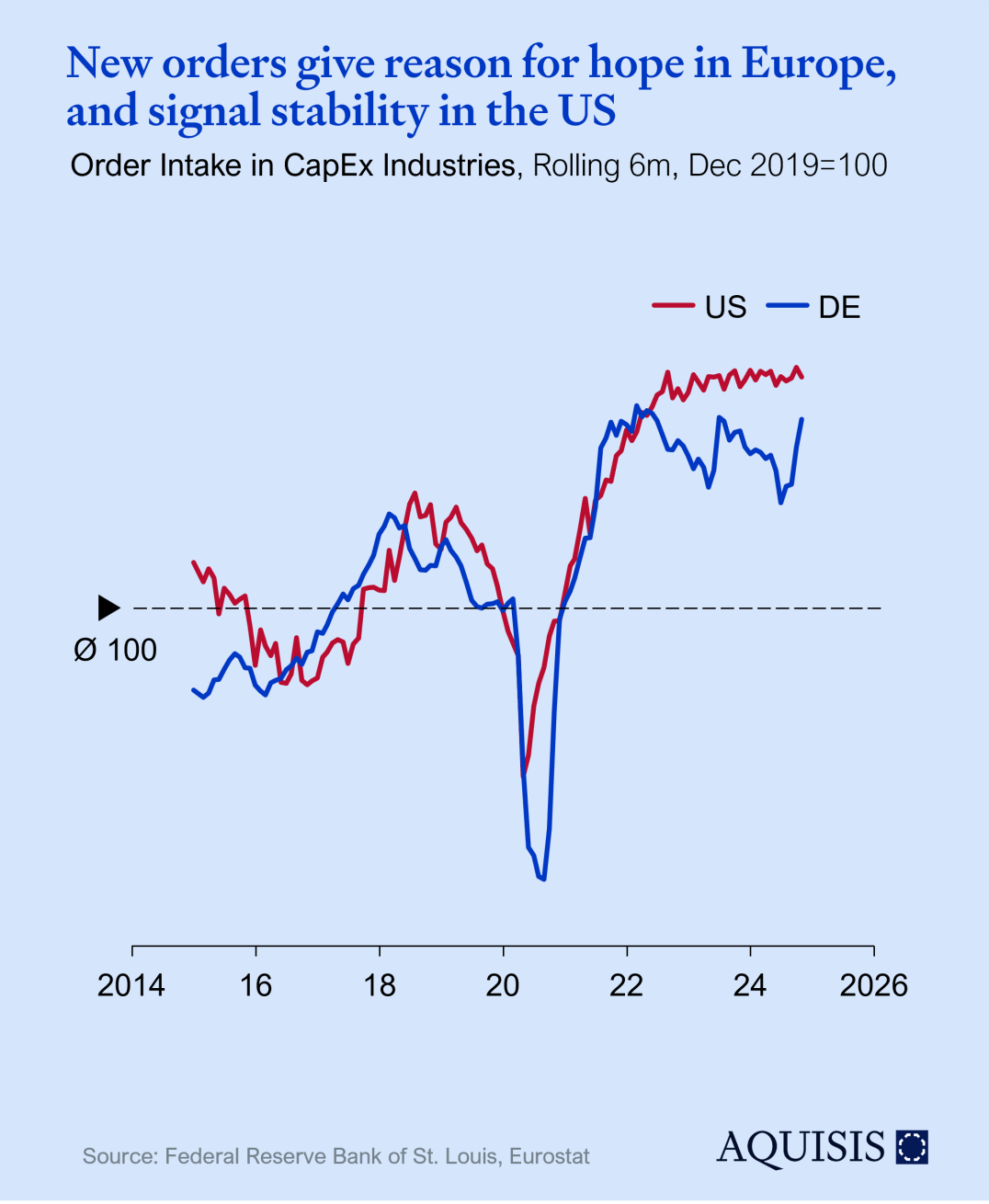
Companies only invest in new equipment if they are confident enough about future demand, making order intake for capex equipment a good leading indicator. The situation in the US has been essentially constant in 2023 and 2024. German new orders are more variable and show a more visible post-Covid backlog effect while slightly trending down since – though staying above the pre-Covid peak.
The outlook for 2025 is quite positive: In the three months to Oct 2024, new orders in Germany reached were 8% higher than in the period in 2023 and reached a level twice recorded before (early 2022 and mid 2023). Leaving aside potential geopolitical curveballs, this gives hope for a strong start into 2025
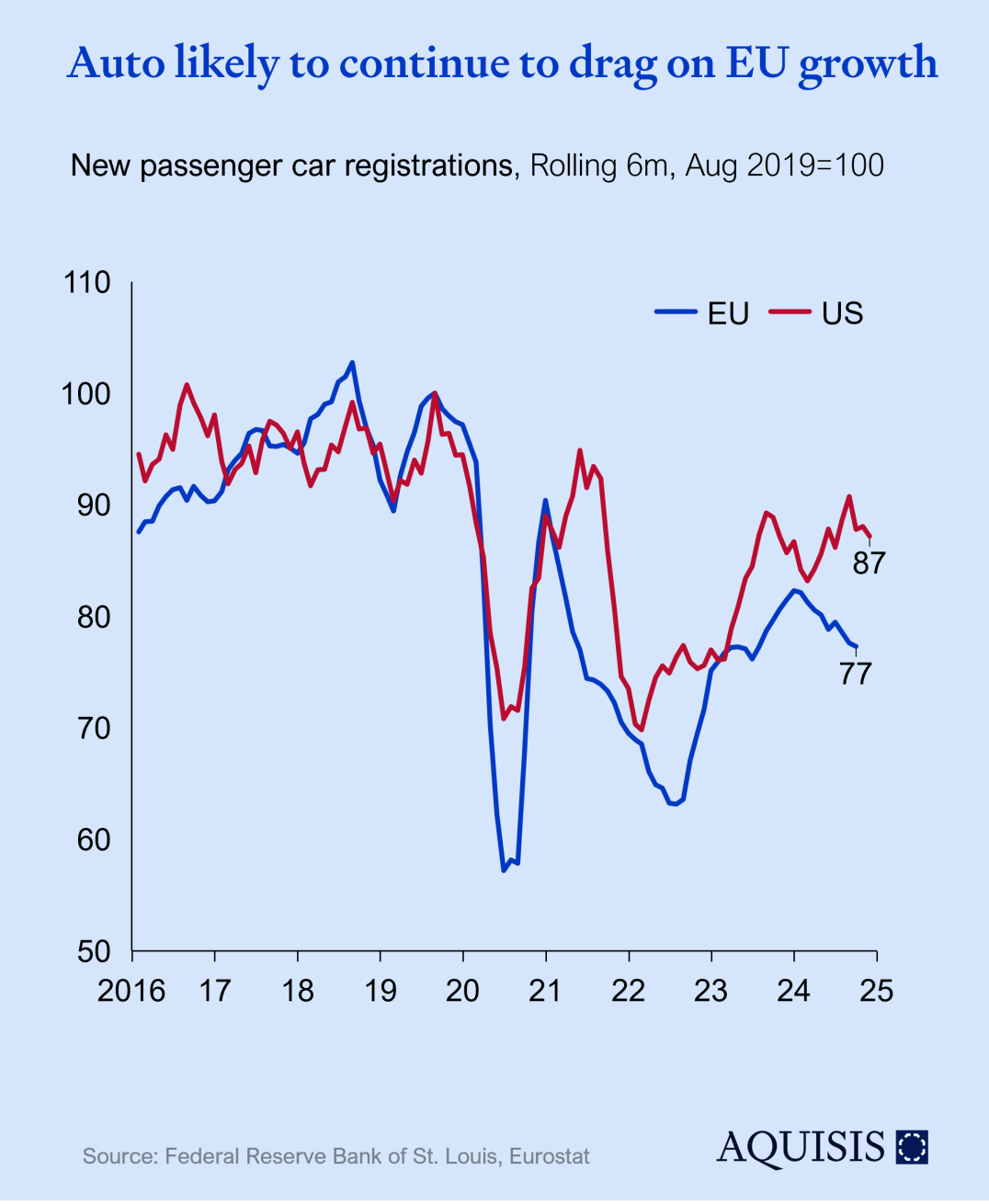
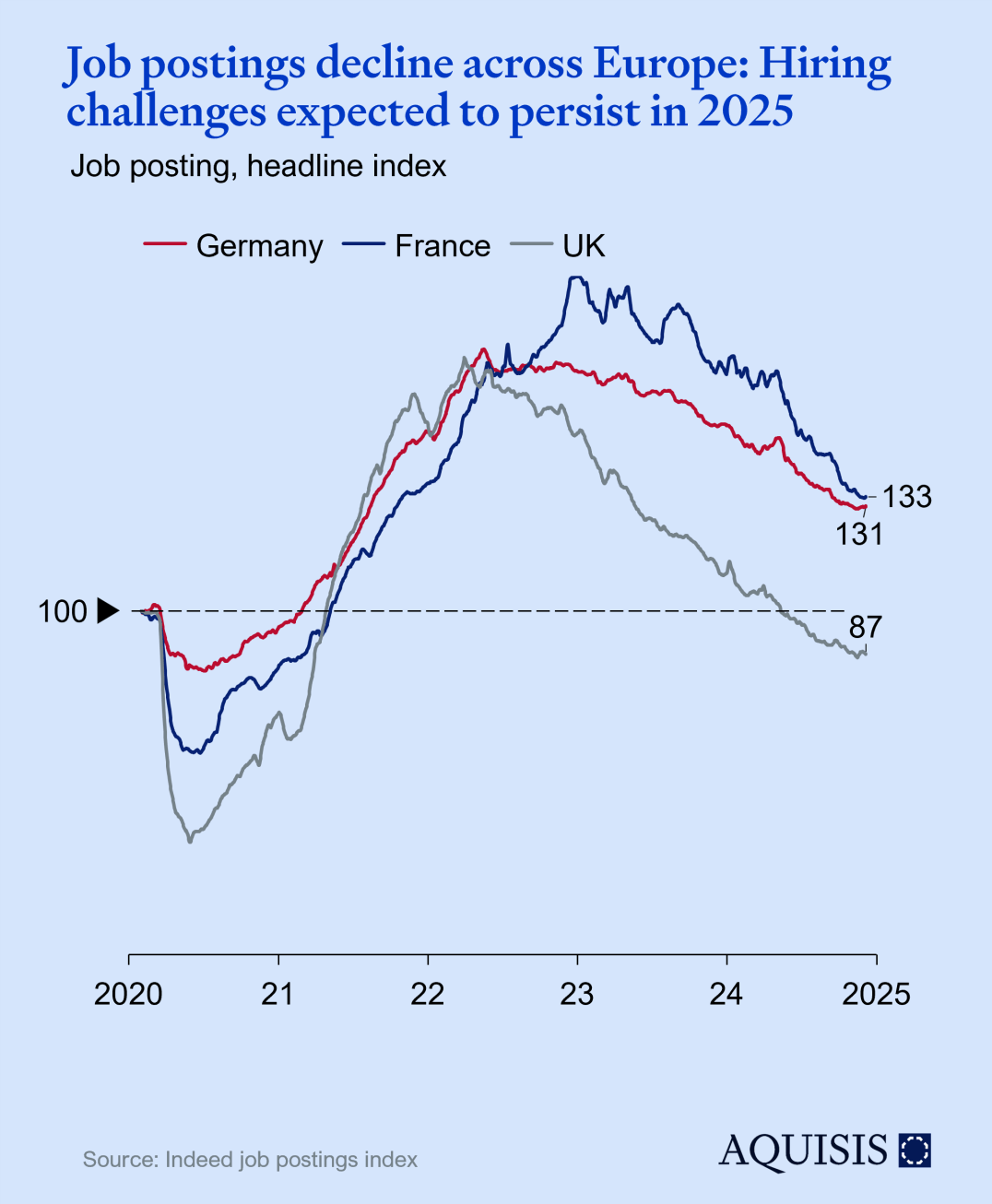
By the same logic as new orders for capex goods indicate manufacturing confidence, vehicle sales indicate consumer confidence – and propel an important European export industry. While the US has almost reached pre-Covid levels of vehicle sales, Europe lost of all the ground gained in the past 2 years. Expectations are for US volumes to continue growing and EU to stay constant. Coupled with European OEM’s struggle to compete with Chinese EVs, and the slow road to obsolescence for important fractions of the European auto value supply chain, we expect a negative growth contribution for the auto sector. On the plus side, order times and inventory levels are mostly normalizing. An optimistic scenario of supportive regulation and European OEMs re-sparking consumer interest could see growth ticking up 2026.
Associate
Managing Partner
No Code Website Builder